- +86 (0) 20-86655668
- info@gionar.com

English

English
March 31 , 2025
The global leather industry produces approximately 8 million tons of waste annually, with only about 20% currently being recycled or repurposed. This startling statistic highlights the urgent need for better leather recycling solutions in our increasingly eco-conscious world. Recycled leather has emerged as one of the most promising sustainable alternatives, offering both environmental benefits and commercial potential.
Many consumers and even manufacturers don’t understand what recycled leather truly is, how it differs from bonded leather, or whether it qualifies as vegan. The durability and application of recycled leather products have triggered more discussions and reflections.
The question of whether leather is recyclable requires that we first understand what “recycling” means for organic materials. Unlike metal or plastic, which can be melted and transformed, leather presents unique challenges and opportunities when it comes to recycling.
From a materials science perspective, leather is mainly composed of collagen fibers that are stabilized through the tanning process. These cross-linked protein structures make the leather durable, but also make it resistant to natural degradation. The same properties that make leather durable also complicate its recyclability.
Mechanical recycling: Pieces of leather are crushed into fibers and then reassembled with adhesives.
Chemical recycling: Breaking down the leather at the molecular level to extract reusable components.
Bio-recycling: The use of enzymes or microorganisms to digest leather waste.
Each approach has advantages and disadvantages in terms of energy demand, quality of output and environmental impact. Due to the relatively low cost, mechanical recycling is currently the dominant method, but emerging methods promise higher quality outputs.
Not all leather products are recyclable. There are several key factors that determine how easy it is to recycle leather items:
Tanning method: plant-tanned leather has higher recovery efficiency than chrome-tanned leather.
Finishes and coatings: Painted or treated surfaces may need to be removed.
Product structure: Mixed materials (such as lining or hardware) need to be separated.
Age and condition: Degraded leather produces lower quality recycled materials.
Industry studies have shown that the recovery rate of post-industrial leather waste (manufacturing waste) reaches 85-90%, while the recovery rate of post-consumer leather products (second-hand products) is only 15-20% due to collection and disposal challenges.
Many fashion brands are now increasingly incorporating recycled leather into their sustainability plans, which has also prompted many leather manufacturers and factories to pay attention to the recyclability of leather. However, the recycling process itself is not without environmental costs – mainly from the energy used during collection, sorting and disposal.
Leather is technically recyclable, but the practical realities of leather recycling reveal both opportunities and difficulties.
The leather recycling industry remains surprisingly fragmented. According to 2023 data from the International Tanning Association:
Europe leads the way in terms of leather recycling infrastructure, with 38 specialist facilities.
There are 22 dedicated leather recycling operations in North America.
Asia’s economies are growing fast, but they still lack centralized systems.
Developing countries often rely on informal upcycling rather than industrial recycling.
Not all leather products are treated equally in the recycling system:
Manufacturing waste (uniform composition)
Unfinished vegetable tanned leather
A minimalist product with no hardware
Shoes (sole separation required)
Jacket (lining and zipper must be removed)
Furniture (challenging due to size issues)
Laminated or coated leather
Products with metal rivets/studs
Items that are seriously contaminated or deteriorated
Many recycling technologies are not commercially viable without subsidies or regulatory mandates due to technical limitations and high costs. With the upgrading of technology and the maturity of effective solutions, the popularity of recycling technology is expected to increase significantly.
Polyurethane (PU) leather, often marketed as an environmentally friendly alternative, comes with a host of recycling challenges.
Finish: polyurethane film (0.1-0.3mm thick)
Fabric backing: usually polyester or cotton
Adhesives: Various binders
This combination makes mechanical separation virtually impossible with current techniques. While the individual ingredients are recyclable in theory, their composite nature makes most PU leather products unrecyclable in practice.
Despite the challenges, there are ways to:
Shred the entire product, producing low-value filler material, and only 20-30% of the input becomes a usable output.
Solvent-based layer separation for the recovery of purest materials with high energy requirements (5-7kWh/kg).
Incineration, with its energy recovery, has an environmental impact and is only feasible where a landfill ban exists.
Several promising developments could improve the recyclability of PU leather:
Polymer design: Use the same plastic series.
Reversible adhesive: allows clean layers to separate.
Can leather handbags be recycled? Yes, but leather handbags face unique recycling challenges due to their complex construction, which is possible if done the right way. Here’s how to dispose of or reuse an old leather bag responsibly.
Yes, but not through curbside recycling.
Leather is biodegradable (if untreated), but most bags have metal zippers, plastic linings, and chemical dyes that complicate recycling.
Only 20% of leather waste is recycled, with the rest going to landfills.
Choose thrift stores, or online resales, or branded recycling programs.
There are companies that specialize in leather recycling, and also look for local shoe/bag repair shops (which usually accept old leather repairs).
Turn an old bag into: a clutch or purse (remove hardware, cut and sew), or a pet accessory (leash, collar or dog bed stuffing).
Crushed into fiber → Used for insulation, automotive interiors or newly bonded leather.
Chemical decomposition → New materials for collagen extraction (rare but emerging).
Do not throw it into regular recycling bins (polluting streams).
Avoid landfills (leather takes more than 50 years to decompose).
Do not burn it (release toxic fumes from dyes/chemicals).
Recycling a leather bag takes time and effort, but donating, upcycling, or using a professional recycler can keep it out of landfills.
Leather belts are easier to recycle than complex leather goods such as handbags because they have less material to mix.
Yes, but not in a regular recycling bin. Pure leather (vegetable tanned) can be biodegradable or reused. Chrome tanned leather (common in cheap belts) contains toxins and is more difficult to recycle, and the metal buckle and plastic liner must first be removed.
You can choose to donate or resell. You can also uprecycle at home, turning an old belt into something else you can use. Industrial recycling methods can also be used.
Belts are one of the easiest leather items to recycle or reuse. If it is in good condition, it can be donated or resold. If damaged, upgrade or send to a professional recycler.
Faux leather (PU, PVC) is difficult to recycle because most types are plastic-based, while vegan leather is relatively easy to recycle.
Yes, but the options are limited.
PU/PVC leather (the most common) is non-biodegradable and is rarely recycled.
Vegan leather (cactus, mushroom, pineapple) may be compostable.
Items with mixed materials (zippers, linings or metal) must be removed first.
The best way to recycle is to choose to donate or resell. Upcycling can also be done at home, transforming faux leather into something else that can be used.
Choose plant-based alternatives (cactus, mushrooms, or pineapple peels).
Buy used (extend the life of existing materials).
Faux leather is difficult to recycle, but donating, upcycling or using a professional program can make it last longer.
Yes, leather wallets can be recycled, but the recycling process depends on the type and structure of the leather.
Plant-tanned leather (natural, biodegradable) is easier to recycle and can be used for composting.
Chrome tanned leather (commonly found in cheap wallets) contains toxins and is more difficult to process.
Mixed materials (plastic ID window, metal buckle, splice) must be separated first.
Leather wallets can be recycled, with donation, upcycling and other recycling options.
Recycled leather is also known as sustainable leather, it is an environmentally friendly material made from repurposed leather scraps and fibers that would otherwise go to waste. It combines sustainability and durability to give discarded leather goods a second life.
The production of recycled leather requires several steps:
Post-industrial waste (leather left over from factories)
Post-consumer trash (old shoes, bags, furniture).
Separate non-leather parts (zippers, plastic, metal).
The leather is ground into fine fibers.
If possible, wash the fibers to remove dyes and chemicals.
Fiber blend:
Natural adhesives (plant latex, starch).
Synthetic adhesive (PU or acrylic to increase strength).
Laminated or molded into a product.
Embossed to mimic the texture of real leather.
Stain or coat for waterproofing.
It could be, but not in its original form.
Contains 30-80% dermal fibers (depending on quality).
The rest are adhesives and fillers (natural or synthetic).
Not as durable as full-grain leather, but more sustainable.
Sustainable – Reduce leather waste in landfills.
Cost effective – cheaper than premium leather.
✔ Vegetarian option – Some brands avoid animal-based adhesives.
Versatile – for bags, shoes, furniture, car interiors.
May contain synthetic adhesives (not 100% biodegradable).
Recycled leather is an environmentally friendly alternative that gives old leather new life. While not as durable as raw leather, it is a great sustainable option for fashion and accessories.
Yes or no, the answer depends on how recycled leather is made:
100% Plant recycled leather = Vegan
Made from recycled fibers + plant adhesives (natural latex, cactus or mushroom based adhesives).
Brands like cactus skin or Mylo (mushroom skin) are vegan leather.
Traditional recycled leather = Not vegan
Contains dermal fragments (from animal hides) and is also commonly used with animal-based glues (although synthetic adhesives may also be used).
Check the label – Find:
“100% plant-based”
“Vegetarian skin”
Certified by PETA/Vegetarian Society
Ask about adhesives – Avoid brands of animal glue or chrome tanned leather waste.
If you want a 100% cruelty-free option:
Cactus leather
Mushroom leather (Mylo, bolt thread)
Pineapple Leather (Pinatex)
Apple Leather (Frumat)
Most recycled leather is not vegan (containing waste from animal sources). Some brands produce vegan recycled leather (using plants + synthetic adhesives).
Although both of them reuse leather waste, they have some similarities and some differences:
Chopped high quality leather waste + plant-based/synthetic adhesive.
Press into sheets (retaining some leather properties).
Ground to fine dust + heavy synthetic glue.
Laminated on fabric/paper backing (such as particleboard for leather).
Recycled leather feels thicker and ages gracefully. Bonded leather has a paper-like backing with cracks at the edges.
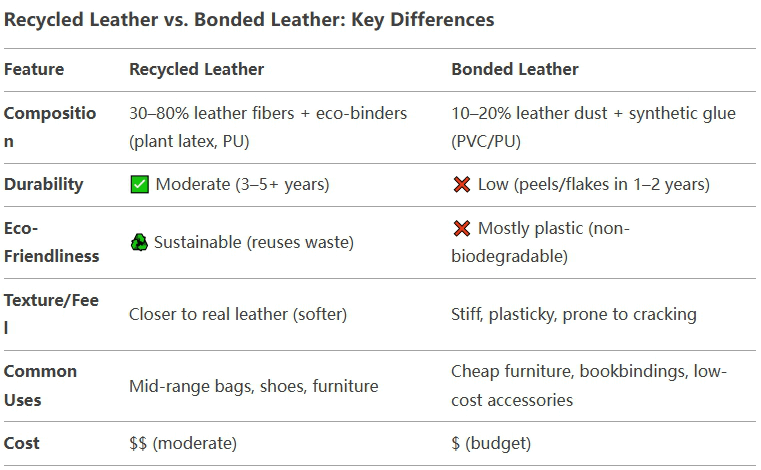
It may be better to opt for recycled leather if you want a more durable, environmentally friendly option. And don’t mind some animal ingredients (unless labeled vegan). Recycled leather is higher quality and more environmentally friendly than bonded leather,
Sustainability and Durability → Recycled leather (if you don’t mind some animal ingredients).
Vegan → Vegan leather (cactus, mushroom or apple leather).
Avoid using bonded leather unless you need a cheap short-term option.
The durability of recycled leather depends on how it is made and used, and can generally be used for 3-8 years.
The life of recycled leather is 3-8 years, which is more durable than bonded leather, but not as durable as premium animal leather. The higher the leather fiber content in recycled leather, the longer the service life.
Reinforcing adhesive (some brands use polyurethane for added strength).
Thicker fabric (more suitable for making bags and furniture).
Uv/waterproof coating (extended outdoor life).
Low leather content (<50%)= Faster wear.
Cheap adhesives (such as PVC) can cause flaking.
Heavy daily use (for example, work boots) will wear it out faster.
Maintain once a year (with a plant-based leather cream).
Avoid excessive moisture (which can weaken the adhesive).
Store properly (avoid direct heat/sun exposure).
Choose good quality or high-end brands.
Recycled leather is durable enough for everyday use, but not for heavy abuse. Proper care can extend the service life of recycled leather.
If you are looking for a bag manufacturer of custom recycled leather handbags, whether your own designs or personal items, accept recycled leather waste for bonded leather production. Leather bag manufacturer Gionar, located in Baiyun District, Guangzhou, China, we have professional designers for you to customize the design of bags, professional production process to solve product quality and mass production, welcome to contact us at any time.
Some of the customized services:
material Genuine Leather Closure Type Open Lining suede…


Mobile Website

Inquires Whatsapp
