- +86 (0) 20-86655668
- info@gionar.com

English

English
April 25 , 2025
Mushroom leather is an innovative vegetarian material made from the root-like network of fungi (mycelium). Although mushroom leather is softer and lighter than animal leather, their durability is still improving. Its greatest advantages are sustainability and biodegradability. At present, mushroom leather is expensive niche products, but with the development of technology, the cost may decrease. The ideal eco-friendly fashion strikes a balance between morality and innovation, offering a promising future for sustainable materials.
Mushroom leather (also known as mycelium leather or fungal leather) is a sustainable alternative to vegetarian animal leather, made from the root-like structure of mushrooms (mycelium). As an environmentally friendly material, it is becoming increasingly popular in industries such as fashion bags and furniture.

Mushroom strains (such as Ganoderma lucidum, oyster or fomentarius)
Disinfected substrates (sawdust, straw, agricultural waste)
Plastic bags or pallets (for controlling growth)
Hydrogen peroxide (for sterilization)
Sterilize the substrate (such as sawdust + straw) by boiling or baking to kill contaminants.
Add mushroom eggs (just like sowing seeds in the soil).
Place the mixture in a dark, damp and warm environment (20-25°C / 68-77°F) for 1-3 weeks.
Fungi (such as Fomes, fomentarius or Ganoderma lucidum mushrooms) grow on organic waste (sawdust, straw) in a controlled laboratory.
The mycelium will grow into a white fibrous network and combine with the substrate.
Once fully planted (dense, spongy texture), remove from the container.
Gently rinse to remove the substrate debris.
The harvested mycelium is washed, compressed and treated with natural adhesives such as plant-based resins.
Flatten and densify between the wooden boards or in a hot press (~70°C / 158°F).
Dry in the sun or dehydrate to a moisture content of approximately 10-15%.
Soak in natural tanning solutions (such as oak tannin or alum) to maintain durability.
Leather-making adopts environmentally friendly methods (without using toxic chemicals such as chromium used in traditional leather).
Optional: Apply plant-based wax or oil (beeswax, small candles) to resist water.
Gently polish smooth or embossed the texture pattern.
If necessary, natural pigments can be used for dyeing.
It can be dyed, embossed, or textured to imitate animal leather (for example, suede, smooth, or granular finish).
The production of mushroom leather (mycelium leather) requires the cultivation and processing of fungal mycelium to make it a durable, leather-like material.
Eco-friendly – Biodegradable, low carbon footprint, and uses the least amount of water.
Vegetarian and cruelty-free – no animal products.
Versatile – It can be made as soft as lambskin or as durable as cowhide.
Hypoallergenic – Free of animal protein, reducing the risk of allergies.
Less durable (currently) – not as scratch-resistant/water-resistant as high-end animal leather.
Limited availability – still in the early stage (small-scale production).
Higher cost – currently more expensive than synthetic vegan leather (but as technology advances, the price may drop).
Yes, mushroom leather can be a great material for making bags, especially if you prioritize sustainability, vegetarian ethics and lightness and comfort. However, its performance depends on the quality of the mycelium material and the processing method.
Lightweight and soft – usually more elastic than traditional leather (similar to sheepskin).
Customizable – It can be dyed, embossed, or textured to imitate luxury leather.
Not very durable (currently) – not as scratch-resistant/water-resistant as high-end calfskin or full-grain leather.
Higher costs – it is still a niche market, so the price is very high.
Care challenge – Traditional leather conditioner cannot be used (plant-based care is required).
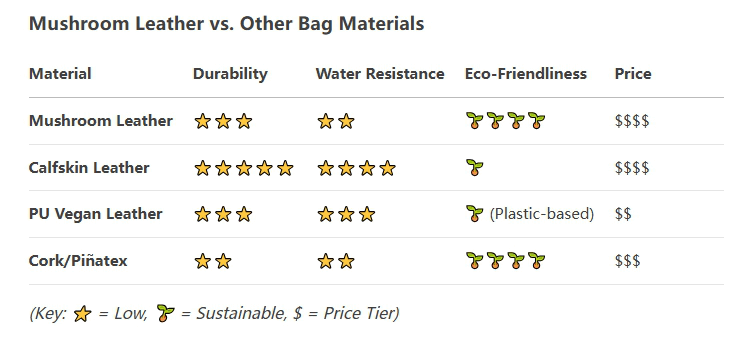
Handbags and minimalist wallets – low-pressure design.
Luxury fashion items – limited edition items .
Leisure/experimental design – Brands such as yoga bags and prototypes.
Heavy bags (such as weight-bearing backpacks).
High-wear areas (shoulder straps, handles), unless reinforced.
Avoid water – use plant-based waterproof sprays (for example, wax mixtures).
Gentle cleaning – Wipe with a damp cloth and mild soap (alcohol-free or solvent-free).
Store properly – Keep in a dust bag, away from moisture/sunlight.
Use algae or coconut oil-based conditioner (not animal-based).
How long does mushroom leather last? Durable enough for mindful use, but not yet for hardcore utility. Mushroom leather is expected to become a sustainable material, but its durability is still lower than that of traditional animal leather or high-end synthetic alternatives at present. With the advancement of laboratories (such as gene-edited mycelium strains), it may soon be comparable to the durability of calfskin.
Medium to low – Softer than calfskin or whole cowhide, it is prone to obvious scratches (similar to lambskin).
The newer engineering version is improving the scratch resistance.
Poor natural performance – absorbs moisture unless treated with wax or plant-based coatings.
Some brands will add a waterproof layer in the bag.
Weaker than animal leather – the mycelium lacks the dense collagen fibers of leather.
Industrial processes (compression, adhesives) can be helpful, but its tear resistance is still relatively poor.
How long does mushroom leather last? 5-10 years of care – degrades faster than cowhide but slower than cheaper PU vegan leather.
Avoid excessive daily use.
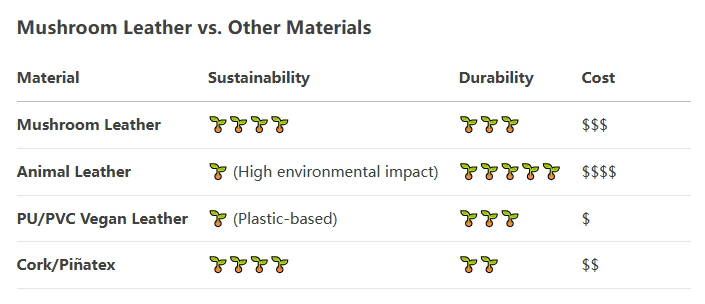
Yes, mushroom leather can be one of the most sustainable leather alternatives available at present, but their ecological impact depends on the production method. Why are mushroom leather sustainable?
Negative carbon: Mycelium absorbs carbon dioxide during its growth process (unlike cowhide, accounting for 14.5% of global emissions).
Minimum water consumption: Only 1% of the water required for animal leather (without pollution from livestock breeding or tanning).
No toxic chemicals: Plant tanning avoids chromium (a carcinogen used in 85% of traditional leathers).
Decompose in compost for 90 to 180 days (in contrast, synthetic vegan leather, such as PU, will shed microplastics).
Growing on agricultural waste: Using sawdust, straw or food by-products as the substrate.
No animals are slaughtered or forests are cut down for grazing (unlike raising cattle).
Yes, mushroom leather is biodegradable, which is one of its greatest ecological advantages over traditional animal leather (treated with toxic chemicals) and synthetic vegan leather (based on plastic).
The root-like structure of mushrooms is 100% organic (like plant fibers).
If the synthetic coating is untreated, it will decompose like food waste.
In the compost bin: 3 to 6 months (in contrast, chrome tanned leather may take over 50 years).
In soil/landfill: 6-12 months (speed depends on humidity/microorganisms).
It does not release microplastics or toxins (unlike PU/PVC vegan leather).
Return nutrients to the soil (unlike synthetic materials).
It must be untreated – some brands add PU/ polyester coating to enhance durability and prevent biodegradation.
Composting setup is needed – home composting posts work, but industrial composting (at higher temperatures) is faster.
Avoid mixed materials – Remove non-biodegradable zippers/linings before composting.
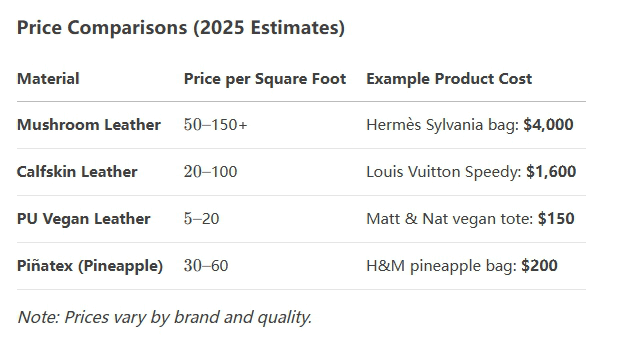
Yes, mushroom leather are currently very expensive – usually more expensive than traditional animal leather or synthetic vegetarian alternatives. Why are mushroom leather so expensive?
Most mycelial leathers are cultivated in the laboratory and the quantity is limited.
The high research and development costs have pushed up the prices.
The growth of mycelium requires a sterile environment, precise humidity/temperature control and manual finishing.
Leather-making and dyeing use environmentally friendly (but more expensive) plant-based methods.
Designer collaboration increases the exclusivity premium.
If you give priority to:
Sustainability (biodegradable, low carbon footprint).
Vegetarian ethics (not harming animals).
Support cutting-edge bio-manufacturing.
Mushroom leather is very expensive now, but they will become easier to buy in the future.
Mushroom leather are a promising sustainable luxury material, but they need to make progress in terms of durability and scalability. At present, it is most suitable for buyers who are fashionable and avant-garde, environmentally conscious and willing to make some trade-offs in terms of durability. With the advancement of technology, it can replace animal leather and synthetic leather in many applications.
Gionar is a leather goods manufacturer with 19 years of industry experience specializing in handbag production, capable of crafting mushroom leather (mycelium-based) handbags and accessories according to client specifications.
Gionar is a professional leather bag manufacturer located in Baiyun District, Guangzhou City, China. It has a modern production factory and a team of experienced artisans, dedicated to providing high-quality customized bag services for global customers.
Related customized services:
material Genuine Leather Closure Type Open Lining suede…


Mobile Website

Inquires Whatsapp
